Interface engineering of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for high-performance lithium metal batteries
Abstract
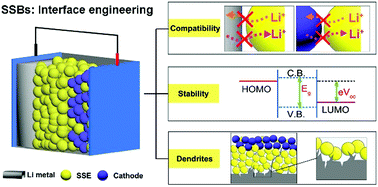
The high fluidity and flammability characteristics of the conventional organic liquid electrolyte make it vulnerable for the currently employed commercial lithium batteries to suffer from potential safety risks and premature cell failure. Replacing liquid electrolytes with inorganic solid-state versions coupled with the employment of Li metal anodes is believed to be ideal for next generation energy storage systems with both high security and high energy density. However, even though several promising solid-state electrolytes possess extremely high ionic conductivity, the issues related to a poor electrode/electrolyte interface are a critical constraint. Herein, interface engineering based on current fundamental understanding, challenges, and opportunities of the interface chemistry between inorganic solid-state electrolytes and electrode materials are presented. Firstly, we focus on the interfacial configuration characteristics and mechanisms, pointing out that the unsatisfactory interfacial compatibility and stability, and the dendrite problem are the main drawbacks in achieving high-performance cells, where the interface contact/wettability, constant interfacial reactions, inadequate interfacial Li+ stripping/plating process, and Li dendrite formation/propagation mechanism will be individually reviewed. Then, the recent research status and trends in ameliorating the electrode/electrolyte interface are systematically examined, including the efforts for component optimization and the architectural design of bulk anodes, electrolytes, cathodes, and the interface engineering construction between them. Moreover, several progressive applications and future research directions of interface chemistry will be proposed, aiming to present a comprehensive and enlightening overview for interface engineering that are relevant for the integration of applicable solid-state Li metal batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...