Probing the effect of P-doping in polymeric carbon nitride on CO2 photocatalytic reduction†
Abstract
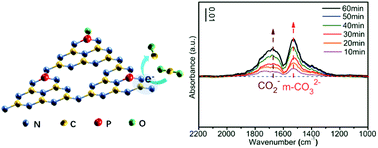
Developing highly efficient photocatalysts is of crucial importance to solve the energy crisis and global warming issues. In this work, a P-doped polymeric carbon nitride (CN) photocatalyst was synthesized by one-step copolymerization of guanidine hydrochloride and phosphonitrilic chloride trimer. The doping of P in CN was found to alter the electronic structure, enhance the charge separation and transfer, and promote the CO2 adsorption and activation, making it an efficient CO2 photoreduction catalyst. At the optimized P dose, the CO evolution amount on P-doped CN reached 0.349 μmol (30 mg, 3 h), which was 3.5 times that of pure CN. The process of CO2 photoreduction on P-doped CN was investigated by in situ FTIR analysis, revealing that P doping could promote the formation of a CO2− intermediate. A possible mechanism has been proposed, which may provide new insights into the effect of non-metal element doping in CN on its CO2 photocatalytic reduction performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...