Computational mechanistic insights into non-noble-metal-catalysed CO2 conversion
Abstract
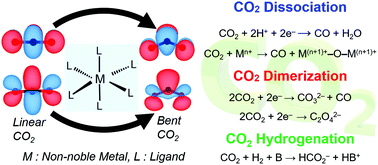
The conversion of CO2 into liquid fuels and value-added fine chemicals is of significant interest for both the environment and the global energy demand. In this frontier article, we highlight viable methods for transforming CO2 into valuable C1 feedstocks and summarize the key mechanistic aspects obtained by in-depth computational investigations of three important pathways of two-electron CO2 reduction: (i) CO2 dissociation to CO (ii) CO2 dimerization to CO32− and CO, and (iii) CO2 hydrogenation to formate. Lastly, we present our outlook on how theoretically obtained mechanistic insights could be translated into strategies for designing efficient non-noble-metal catalysts for CO2 reduction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Frontier and Perspective articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...