Comparison of the ionic conductivity properties of microporous and mesoporous MOFs infiltrated with a Na-ion containing IL mixture†
Abstract
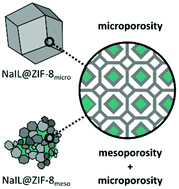
IL@MOF (IL: ionic liquid; MOF: metal–organic framework) materials have been proposed as a candidate for solid-state electrolytes, combining the inherent non-flammability and high thermal and chemical stability of the ionic liquid with the host–guest interactions of the MOF. In this work, we compare the structure and ionic conductivity of a sodium ion containing IL@MOF composite formed from a microcrystalline powder of the zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF), ZIF-8 with a hierarchically porous sample of ZIF-8 containing both micro- and mesopores from a sol–gel synthesis. Although the crystallographic structures were shown to be the same by X-ray diffraction, significant differences in particle size, packing and morphology were identified by electron microscopy techniques which highlight the origins of the hierarchical porosity. After incorporation of Na0.1EMIM0.9TFSI (abbreviated to NaIL; EMIM = 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium; TFSI = bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide), the hierarchically porous composite exhibited a 40% greater filling capacity than the purely microporous sample which was confirmed by elemental analysis and digestive proton NMR. Finally, the ionic conductivity properties of the composite materials were probed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The results showed that despite the 40% increased loading of NaIL in the NaIL@ZIF-8micro sample, the ionic conductivities at 25 °C were 8.4 × 10−6 and 1.6 × 10−5 S cm−1 for NaIL@ZIF-8meso and NaIL@ZIF-8micro respectively. These results exemplify the importance of the long range, continuous ion pathways contributed by the microcrystalline pores, as well as the limited contribution from the discontinuous mesopores to the overall ionic conductivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...