A mixed-valence diruthenium(ii,iii) complex endowed with high stability: from experimental evidence to theoretical interpretation†
Abstract
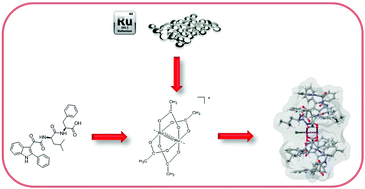
We herein report the synthesis and multi-technique characterization of [Ru2Cl((2-phenylindol-3-yl)glyoxyl-L-leucine-L-phenylalanine)4], a novel diruthenium(II,III) complex obtained by reacting [Ru2(μ-O2CCH3)4Cl] with a dual indolylglyoxylyl dipeptide anticancer agent. We soon realised that the compound is very stable under several different conditions including aqueous buffers or organic solvents. It is also completely unreactive toward proteins. The high stability is also suggested by cellular experiments in a glioblastoma cell line. Indeed, while the parent ligand exerts high cytotoxic effects in the low μM range, the complex is completely non-cytotoxic against the same line, most probably because of the lack of ligand release. To investigate the reasons for such high stability, we carried out DFT calculations that are fully consistent with the experimental findings. The results highlight that the stability of [Ru2Cl((2-phenylindol-3-yl)glyoxyl-L-leucine-L-phenylalanine)4] relies on the nature of the ligand, including its steric hindrance that prevents the reaction of any nucleophilic group with the Ru2 core. Ligand displacement is the key step to allow reactivity with the biological targets of metal-based prodrugs. Accordingly, we discuss the implications of some important aspects that should be considered when active molecules are chosen as ligands for the synthesis of paddle-wheel-like complexes with medicinal applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...