New Li–Mg phosphates with a 3D framework: experimental and ab initio calculations
Abstract
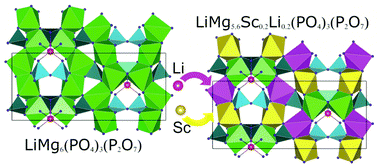
Two new lithium–magnesium phosphates LiMg6(PO4)3(P2O7) and Li(Mg5.62Sc0.19Li0.19)(PO4)3(P2O7) were synthesized by a solid-phase method. Using high-resolution time-of-flight neutron powder diffraction (TOF NPD) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), we established that these phosphates have a Pnma orthorhombic structure with the cell parameters a = 9.14664(5) Å, b = 18.83773(8) Å, c = 8.27450(4) Å, and V = 1425.71(1) Å3 and a = 9.14516(5) Å, b = 18.84222(9) Å, c = 8.28204(4) Å, and V = 1427.12(1) Å3, respectively. The crystal structures can be described by stacking of the [Mg6O18]∞ or [Mg5.62Sc0.19Li0.19O18]∞ wavy layers, which are parallel to the (100) direction and interconnected through PO4 tetrahedra and P2O7 groups to form a 3D-framework. The Li atoms are located in large tunnels formed in a 3D lattice, which contributes to lithium diffusion. AC impedance spectroscopy analysis shows that LiMg6(PO4)3(P2O7) and Li(Mg5.62Sc0.19Li0.19)(PO4)3(P2O7) have a Li ion conductivity of 3.6 × 10−4 S cm−1 and 1.7 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 950 °C, with an activation energy of 1.28 eV and 1.55 eV, respectively. NMR MAS studies confirmed the coexistence of pyro- and orthogroups in the structure of both phases and two lithium positions in Li(Mg5.62Sc0.19Li0.19)(PO4)3(P2O7). The first-principles method was used to study the electronic structure and stability of the two phases. The calculated formation enthalpies demonstrated that Sc is a stabilizing impurity in LiMg6(PO4)3(P2O7), while a strong destabilization of olivine LiMgPO4 is observed upon doping with Sc. This explains the failure to synthesize Sc-doped olivine. The new phosphate LiMg6(PO4)3(P2O7) is a dielectric with a band gap of 5.35 eV, which decreases to 4.85 eV due to the appearance of a localized Sc 3d peak upon doping with Sc. These findings are consistent with the results obtained by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The new phase may be a good optical matrix similar to LiMgPO4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...