The big effect of a small change: formation of CuO nanoparticles instead of covalently bound Cu(ii) over functionalized mesoporous silica and its impact on catalytic efficiency
Abstract
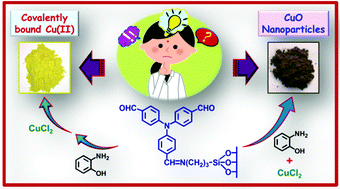
Two different heterogeneous catalysts, one with Cu(II) covalently bonded to functionalized mesoporous silica (FMS-Cu(II)) and another with CuO nanoparticles immobilized over the same silica (FMS-CuO-np), have been synthesized by a common route but with a minor alteration in the sequence of addition of reagents. It is interesting to find that by merely changing the order of the addition of reagents Cu(II) can be incorporated into the framework in two different forms. In one case Cu(II) binds to the N and O donor centers present in the functionalized material whereas in the other case CuO nanoparticles are generated in situ. The materials have been thoroughly characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, nitrogen adsorption/desorption, transmission electron microscopy, thermal analysis, FT-IR spectroscopy, solid state MAS-NMR spectroscopy and atomic absorption spectrophotometric studies. The synthesized products have been examined for their catalytic efficiencies in the oxidation of olefins, as a model case. Styrene, α-methyl styrene, cyclohexene, trans-stilbene and cyclooctene have been used as substrates in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide as the oxidant in acetonitrile medium under mild conditions. The products of the catalytic reactions have been identified and estimated by gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The rate of conversion of the substrates for both the catalysts is high and the selectivity is also good. But from comparative studies, it is found that FMS-CuO-np which contains CuO nanoparticles shows better efficiency than FMS-Cu(II). The catalysts have been recycled for five catalytic cycles without showing much decrease in their catalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...