Color modulation by selective excitation activated defects and complex cation distribution in Zn1−xMgxAl2O4 nanocrystals†
Abstract
Complex cation distribution in spinel solid solution, fosters defect generation and permutates the optical properties. To scrutinize the effect on structural properties, viz. the cation distribution and defect states upon substitution of Zn with Mg; and to tune the emission properties, Zn1−xMgxAl2O4 (0.01 ≤ x ≤ 0.30) nanocrystals are synthesized. The nanocrystals show increased inversion and generation of multiple defects, namely zinc vacancies, zinc interstitials, oxygen vacancies and antisite defects with increasing Mg content, which thereby impacts the optical band gap. Pentahedral coordination in addition to tetra- and octahedral coordination of Al has been observed, which infers the presence of oxygen vacancies and dangling bonds. Moire fringes formation has intimated the presence of two or more crystal lattices with higher Mg substitution. Band-to-band and defect-assisted photoluminescence shows the role of multiple defects, especially 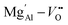 defect clusters, in deciphering the properties of the resulting crystals. Color change from bluish-white to pink has been achieved depending upon the excitation wavelength and emission mechanism, as proposed through a band model schematic. The presented study may be beneficial for designing the Zn1−xMgxAl2O4 nanocrystals with optimized emission properties.
defect clusters, in deciphering the properties of the resulting crystals. Color change from bluish-white to pink has been achieved depending upon the excitation wavelength and emission mechanism, as proposed through a band model schematic. The presented study may be beneficial for designing the Zn1−xMgxAl2O4 nanocrystals with optimized emission properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...