Hypervalent organoiodine(v) metal–organic frameworks: syntheses, thermal studies and stoichiometric oxidants†
Abstract
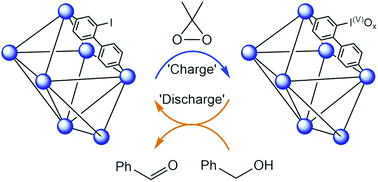
Iodinated analogues of the highly porous IRMOF-9 and UiO-67 frameworks were prepared and post-synthetically oxidised with dimethyldioxirane (DMDO). Analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed promotion to the iodine(V) state and detailed differential scanning calorimetry-thermal gravimetric analysis (DSC-TGA) showed the hypervalent metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) undergo exothermic elimination at ∼200 °C with XPS showing hypervalency is maintained. The hypervalent MOFs are active heterogeneous reagents in sulfoxidation and alcohol oxidation reactions. The crystallinity and porosity of the MOFs were maintained following post-synthetic oxidation, thermolysis and after the heterogeneous reactions, as shown by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and gas adsorption analyses. This work showcases the unique ability MOFs hold for studying chemical reactions and the potential for hypervalent organoiodine MOFs as reuseable oxidants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...