An unprecedented polyhydroxycarboxylic acid ligand bridged multi-EuIII incorporated tellurotungstate and its luminescence properties†
Abstract
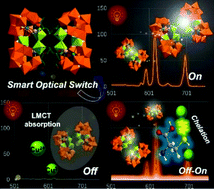
The first polyhydroxycarboxylic acid ligand bridged multi-EuIII-incorporated tellurotungstate K14H10[Eu4(H2O)4W6(H2glu)4O12(B-α-TeW9O33)4]·60H2O (H6glu = D-gluconic acid) (1) was synthesized via an organic ligand-driven self-assembly strategy. The polyhydroxycarboxylic acid ligand bridged tetrameric polyoxoanion [Eu4(H2O)4W6(H2glu)4O12(B-α-TeW9O33)4]24− in 1 can be viewed as an aggregation of four trivacant Keggin [B-α-TeW9O33]8− fragments and an innovative heterometallic [Eu4(H2O)4W6(H2glu)4O12]8+ cluster, in which four high-coordinate polyhydroxy flexible H2glu4− ligands chelate W and Eu centers through carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, giving rise to a heterometallic cluster. The hexagonal packing of the tetrameric polyoxoanions in 1 along the c axis provides excellent porous channels, which greatly increases the specific surface area of the whole framework and may be of benefit for fluorescence sensing in aqueous solution. 1 can function as a “turn-off” luminescence sensor to detect Cu2+ ions in aqueous solution. The limit of detection (LOD) of the 1-sensor is 8.82 × 10−6 mM, which is the lowest among the reported polyoxometalate-based fluorescence sensors. As for the Cu2+-quenching system, it can function as an “off–on” sensor to detect cysteine in an aqueous system, affording a LOD of 1.75 × 10−4 mM. This work opens up an avenue to broaden the applications of polyoxometalate-based materials in the optical intelligence detection field.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...