A facile synthesis of a NiMoO4@metal-coated graphene-ink nanosheet structure towards the high energy density of a battery type-hybrid supercapacitor†
Abstract
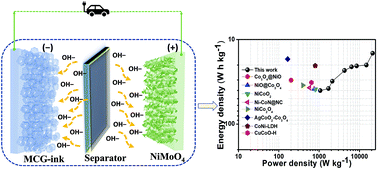
Recently, reagent-based electrode materials (urea, ammonium fluoride, hexamethylenetetramine, L-cysteine, acetic acid, and triethylamine) have received great attention in numerous applications (e.g., solar cells, fuels cells, and battery-type hybrid supercapacitors (BHSCs)). Herein, we designed a wrinkle-type nanosheet structure with a mixture of NiMoO4 using triethylamine via a hydrothermal synthesis. The dual metal ions of Ni2+/Ni3+ and Mo2+/Mo3+ can significantly boost the energy storage performance by the support of triethylamine. NiMoO4 was deposited onto a nickel foam substrate without any binders, and the electrode exhibited a high specific capacitance/capacity of 415.66 F g−1 (249.4 mA h g−1) at 8 mA cm−2 with a good long-term cycling performance over 5000 cycles. Moreover, we assembled flexible HSCs (NiMoO4@MCG-ink) as the core, and the outer material delivered a high specific energy of 40.14 W h kg−1 at 1066.39 W kg−1. The HSC device demonstrated excellent long-term durability with a capacity retention of 99%, and various bending conditions were also tested for flexibility of the device after 5000 cycles. Furthermore, a series of two HSC devices were efficient to light up red and green light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for about 60 minutes, indicating its potential applications in energy storage devices. Hence, our work provides new insights into the preparation of new electrode materials for high energy storage performance of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and SCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...