Graphene quantum dots: efficient mechanosynthesis, white-light and broad linear excitation-dependent photoluminescence and growth inhibition of bladder cancer cells†
Abstract
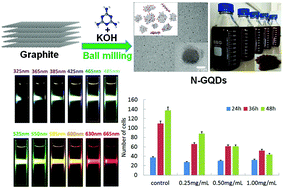
Heteroatom-doped graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have attracted considerable attention due to their potential applications as luminescent materials and in biology. In this work, we developed a solvent-free gram-scale mechanochemical method for the preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) with the highest solubility (31 mg mL−1) in water reported to date. Commercial graphite was sheared and cut through grinding with solid melamine and then ground with solid KOH to get sub-5 nm-sized, 1–3-layered N-GQDs. Notably, these N-GQDs exhibit white-light emission and broad excitation-dependent full-color photoluminescence from 463 nm to 672 nm. When the excitation light ranged from 325 nm to 485 nm, these mechanochemically obtained N-GQDs exhibited bright white-light emission. Intriguingly, the change in the emission wavelength has two-stage linear relationships with the change in the excitation wavelength, and the inflection point is at 580 nm (excited at 550 nm). The difference between the emission and excitation wavelengths decreases from 138 to 12 nm, which also shows two-stage linear relationships with the change in the excitation wavelength. It is notable that their PL quantum yields are high, up to 26.6%. Furthermore, we studied the inhibitory effect of as-obtained N-GQDs on bladder cancer cells (UMUC-3); as a result, with the increase of the concentration of N-GQDs, the proliferation of cancer cells was obviously prohibited.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...