CNN pincer ruthenium complexes for efficient transfer hydrogenation of biomass-derived carbonyl compounds†
Abstract
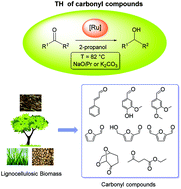
The ligand HCNNOMe (6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-aminomethylpyridine) is easily prepared from the commercially available 6-(4-methoxyphenyl)pyridine-2-carbaldehyde by the reaction of hydroxylamine and hydrogenation (H2, 1 atm) with Pd/C. The pincer complexes cis-[RuCl(CNNOMe)(PPh3)2] (1) and [RuCl(CNNOMe)(PP)] (PP = dppb, 2; and dppf, 3) are synthesized from [RuCl2(PPh3)3], HCNNOMe and PP (for 2 and 3) in 2-propanol with NEt3 at reflux and are isolated in 85–93% yield. Carbonylation of 1 (CO, 1 atm) gives [RuCl(CNNOMe)(CO)(PPh3)] (4) (79% yield) which cleanly reacts with Na[BArf4] and PCy3, affording the cationic trans-[Ru(CNNOMe)(CO)(PCy3)(PPh3)][BArf4] (5) (92% yield). These robust pincer complexes display remarkably high catalytic activity in the transfer hydrogenation (TH) of lignocellulosic biomass carbonyl compounds, using 2-propanol at reflux in a basic medium (NaOiPr or K2CO3). Thus, furfural, 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural and Cyrene are reduced to the corresponding alcohols with 2 and 3, at S/C in the range of 10 000–100 000, within minutes or hours (TOF up to 1 500 000 h−1). The monocarbonyl complex 5 was found to be extremely active in the TH of cinnamaldehyde, vanillin derivatives and ethyl levulinate at S/C in the range of 10 000–50 000. Vanillyl alcohol is also obtained by the TH of vanillin with 5 (S/C = 500) in 2-propanol in the presence of K2CO3.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...