CfbA promotes insertion of cobalt and nickel into ruffled tetrapyrroles in vitro†
Abstract
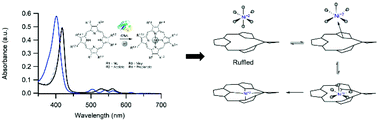
The nickel chelatase CfbA is the smallest member of the chelatase family, but the mechanism by which this enzyme inserts nickel into sirohydrochlorin is unknown. In order to gain mechanistic insight, metal binding, tetrapyrrole binding, and enzyme activity were characterized for a variety of substrates using several spectroscopic and computational approaches. Mass spectrometery and magnetic circular dichroism experiments revealed that CfbA binds an octahedral, high-spin metal substrate. UV/Vis absorption spectroscopy demonstrated that the enzyme binds a wide range of tetrapyrrole substrates and perturbs their electronic structures. Based upon activity assays, CfbA promotes insertion of cobalt and nickel into several tetrapyrroles, including cobalt insertion into protopophyrin IX. Finally, density functional theory models were developed which strongly suggest that observed spectral changes upon binding to the enzyme can be explained by tetrapyrrole ruffling, but not deprotonation or saddling. The observation of an octahedral, high-spin metal bound to CfbA leads to a generalization for all class II chelatases: these enzymes bind labile metal substrates and metal desolvation is not a rate-limiting step. The conclusion that CfbA ruffles its tetrapyrrole substrate reveals that the CfbA mechanism is different from that currently proposed for ferrochelatase, and identifies an intriguing correlation between metal substrate specificity and tetrapyrrole distortion mode in chelatases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...