Spinel copper–iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles with cooperative Cu(i) and Cu(ii) sites for enhancing the catalytic transformation of 1,2-propanediol to lactic acid under anaerobic conditions†
Abstract
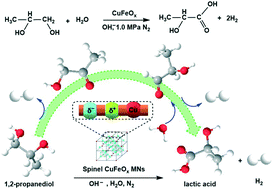
The aerobic catalytic oxidation of 1,2-propanediol (PDO) over non-noble metal (e.g. Cu) based catalysts usually suffers serious C3 product dissociation at high temperature, thus showing low lactic acid (LA) selectivity. Here, an alternative anaerobic catalysis strategy over spinel copper–iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles (CuFeOx MNs) with the coexistence of Cu(I) and Cu(II) dual sites is developed for the catalytic transformation of PDO to LA with a quantitative yield of co-product H2 in basic aqueous solution. The absence of O2 is beneficial for enhancing LA production in comparison with the presence of O2. The synergy between Cu(I) and Cu(II) sites in CuFeOx MNs is vital for improving the catalytic performance as compared to Cu2O or CuO catalysts with Cu(I) or Cu(II) sites alone. Cu1Fe1Ox MNs with a Cu/Fe mole ratio of 1/1 exhibit 94.5% LA selectivity and 72.6% PDO conversion at 160 °C for 8 h. Experimental results and DFT calculations suggest that the spinel CuFeOx MN based catalytic PDO transformation follows a favorable pathway of PDO → hydroxyacetone → lactaldehyde → lactic acid for LA production. In addition to the catalytic PDO transformation, the use of CuFeOx MNs can be extended to favor high activity and selectivity in the catalytic transformation of glycerol to LA (98.5% selectivity) and ethylene glycol to glyceric acid (97.8% selectivity). This work highlights the design of an alternative non-noble metal-based CuFeOx MN catalyst for efficiently catalyzing the transformation of bio-based polyols into value-added carboxylic acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...