Cu oxo nanoclusters for direct oxidation of methane to methanol: formation, structure and catalytic performance
Abstract
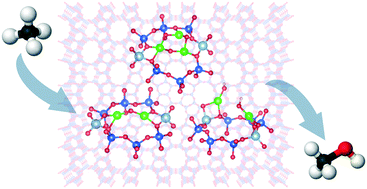
Cu oxo nanoclusters hosted in microporous solids have emerged in the past decades as promising materials for catalyzing the selective conversion of methane to methanol. In this minireview, we highlight the activity of Cu-zeolite materials in the selective oxidation of methane to methanol, and discuss the mechanism of this reaction over different Cu-oxo structural proposals. We aim to offer a comprehensive picture of recently published spectroscopy and theoretical studies which tackled the structure–activity relationships of Cu-oxo nanoclusters. Here it is discussed how the topological diversity of zeolites and other factors influence the formation and stabilization of Cu-oxo motifs, as well as their ability to activate CH4 at mild temperatures. Finally, we also give a brief overview on the catalytic performance of Cu-oxo clusters hosted in metal organic frameworks. At the end of this minireview, we summarize the main conclusions extracted from the literature evaluation, and we provide a brief outlook on the research opportunities in this field.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...