Facile surface improvement of LaCoO3 perovskite with high activity and water resistance towards toluene oxidation: Ca substitution and citric acid etching†
Abstract
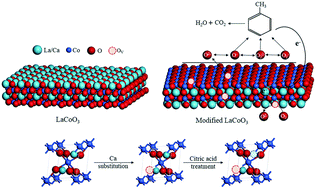
Thermal catalytic oxidation is regarded as an effective technique to eliminate volatile organic compounds (VOCs), whereby perovskite-type oxides have been reported as low-cost and highly efficient transition metal catalysts. In this study, we employ two facile modification methods, i.e., Ca substitution and citric acid etching, to further improve the catalytic activity of LaCoO3 perovskite for toluene oxidation. The Ca-substituted LaCoO3 (La0.9Ca0.1CoO3) and citric acid-etched LaCoO3 (LaCoO3–CA) show T90 values at 220 and 215 °C, respectively, which are substantially lower than that of pristine LaCoO3 (305 °C). When LaCoO3 is modified by both Ca substitution and citric acid etching, i.e., La0.9Ca0.1CoO3–CA, the T90 further decreases to 202 °C, even lower than that of the commercial catalyst 0.5 wt% Pt/Al2O3 (208 °C). In terms of specific reaction rate at 200 °C, the activity of the above catalysts is also enhanced as follows: LaCoO3 (0.14 μmol s−1 m−2) < La0.9Ca0.1CoO3 (0.31 μmol s−1 m−2) < LaCoO3–CA (0.47 μmol s−1 m−2) < La0.9Ca0.1CoO3–CA (0.63 μmol s−1 m−2). The effects of Ca substitution and citric acid etching are discussed in light of the crystal structure, morphology, and lattice defects. On the one hand, Ca substitution and citric acid etching increase the specific surface area and pore volume, which facilitate the contact between toluene and active sites. On the other hand, these methods produce more oxygen vacancies, enhance the reducibility, and facilitate the adsorption of oxygen. The above merits result in the increase in the specific reaction rate. The modified catalysts show a better water resistance than pristine LaCoO3. As verified in the H2O-TPD characterization, this phenomenon is ascribed to the generation of surface hydroxyl groups, which are beneficial for toluene oxidation at high humidity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...