Facile hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde to cinnamyl ether by employing a highly re-usable “dip-catalyst” containing Pt nanoparticles on a green support†
Abstract
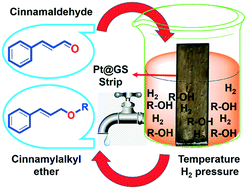
An active, selective, and reusable catalyst, which enables the production of organic fine chemicals, with potential environmental and industrial applications is highly desirable. The fabrication and application of a ‘dip-catalyst’ containing Pt nanoparticles (2–3 nm) on the surface of a green cellulosic support (GS) obtained from the jute plant (Corchorus genus) stem (Pt@GS) is described. TEM revealed spherically shaped Pt nanoparticles distributed throughout the cellulose matrix of the jute strips with an average diameter 2–3 nm which was supported by high angle annular dark-field scanning TEM (HAADF-STEM) study. Cinnamaldehyde can be catalytically hydrogenated to selectively produce cinnamyl ether using a series of alcohols with molecular hydrogen. The effect of the cellulosic support and its superiority compared to other metal oxide supports have been thoroughly studied. Deuterium labelling studies are conducted to investigate the effect of the H/D exchange pattern on cinnamyl methyl ether. The Pt@GS system displays excellent recyclability for multiple reaction cycles without losing its original reactivity; no severe damage to the surface of the support is detected.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...