Palladium dispersion effects on wet methane oxidation kinetics†
Abstract
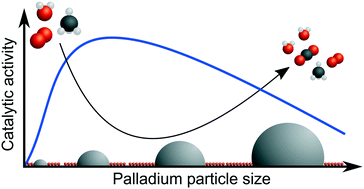
The catalytic activity for dry and wet methane oxidation over a series of palladium–alumina catalysts with palladium loadings from 0.23 to 3.6 wt% Pd and systematically varied PdO dispersions from 8.1 to 39% was evaluated by flow reactor measurements and compared with multiscale simulations. The catalysts were prepared by industrially relevant incipient wetness impregnation followed by controlled calcination to provide similar active surface area with a realistic contact between active PdO nanoparticles and the alumina support. Kinetic analysis reveals that in wet conditions, the apparent activation energy for methane oxidation decreases as the PdO particle size increases as opposed to dry conditions where it increases. Active sites at the rim of the PdO particles in contact with the alumina support seem to contribute more to the overall activity under dry conditions but are more sensitive to wet conditions than PdO sites farther away from the rim. This sensitivity is likely due to more severe blocking by hydroxyl groups formed by water dissociation and reversed spillover. Simulations support that PdO bound hydroxyls well may form under the present reaction conditions. It is envisaged that the design of palladium–alumina catalysts for high methane turn-over frequency should target high but not too high PdO dispersion, i.e., the PdO particles should not be smaller than about 2 nm, as to balance water tolerance and palladium utilisation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...