Computational investigation of the ligand effect on the chemo/regioselectivity and reactivity of cobalt-catalysed hydroformylation†
Abstract
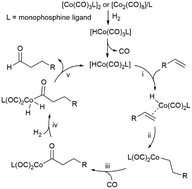
The ligand effect on the chemo/regioselectivity and reactivity of cobalt-catalysed hydroformylation has been discussed. The results of the unmodified cobalt carbonyl catalyst showed that the regioselectivity of the terminal alkene substrate was mainly affected by the steric hindrance of the bulky alkyl substitution group and was insensitive to the elongation of the carbon chain. Regarding the addition of Co–H onto the alkene, modifying the cobalt carbonyl catalyst with a phosphine ligand led to more distinct differences between the Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov pathways with respect to both the energy barrier and the reaction free energy. Among the four selected phosphines, PBu3 and a5-PhobPC5 with large Tolman cone angles favoured anti-Markovnikov-type Co–H addition, which is beneficial for the generation of a linear product. The modification with phosphine also promoted the oxidative addition of H2 on the Co(I) centre by lowering the energy barrier of H2 splitting and generating a more stable Co(III)-dihydride complex but retarded the reductive elimination step by elevating its activation energy and reaction energy. On the whole, the hydroformylation mechanism is similar for both modified and unmodified cobalt carbonyl catalysts. Moreover, PBu3 modification on the catalyst does not intrinsically change the chemoselectivity of alkene but indeed improves the subsequent alcohol and formic ester formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...