Investigation of the deactivation behavior of Co catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis using encapsulated Co nanoparticles with controlled SiO2 shell layer thickness†
Abstract
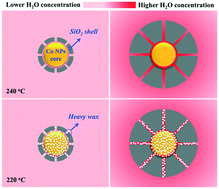
The stability of cobalt catalysts in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS) is one of the most challenging issues, which needs to be solved for their industrial applications. Herein, a series of model silica-encapsulated core–shell Co@SiO2 catalysts have been synthesized with the SiO2 shell layer having different thicknesses. The results show that the thickness of the porous silica layer and the reaction temperature play crucial roles in the search for the origin of catalyst deactivation. At a high temperature (240 °C), the Co@SiO2 catalyst exhibits high catalytic activity, producing a high water vapor concentration inside the catalyst particles together with a higher content of light hydrocarbons. Therefore, the oxidation of metallic Co is the dominant deactivation behavior as a thinner shell layer facilitates water vapor diffusion out of the catalyst surface and the pore channels to alleviate catalyst deactivation. At a low temperature (220 °C), the Co@SiO2 catalyst initially exhibits relatively high catalytic activity and then, it deactivates rapidly, which is mainly attributed to the blocking of the pore channels of the silica layer and the covering of the catalyst active sites by heavier hydrocarbons, leading to the inefficient access of syngas to the active sites. Note that a thinner SiO2 shell layer has a much lower effect on alleviating catalyst deactivation due to wax accumulation. As a result, the 40Co@SiO2 catalyst at 240 °C exhibits excellent stability with almost ∼100% CO conversion due to its efficient prevention of metallic Co oxidation and pore channel blocking with its thinner shell layer. Thus, this proposed new strategy can provide viable information to elucidate the catalyst deactivation behavior and therefore guide the development of stable cobalt catalysts for applications in the FTS reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...