Ru–Ni/Al2O3 bimetallic catalysts with high catalytic activity for N-propylcarbazole hydrogenation†
Abstract
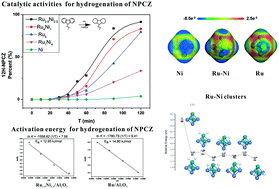
The catalytic hydrogenation of liquid organic hydrogen carriers (LOHCs) is one of the key steps towards large-scale applications. The use of a large amount of noble metals in hydrogenation factories would increase the total cost of the LOHC technology. The partial replacement of ruthenium by another transition metal, i.e., Ni is a potentially effective method. The synthesis and characterization of 5 wt% RuxNi5−x/Al2O3 (x = 0, 1, 2.5, 4, and 5) bimetallic catalysts and their catalytic performance for the hydrogenation of N-propylcarbazole are reported. All catalysts were prepared by a wet chemistry method using a rapid sodium borohydride reduction of the Ni2+ and Ru3+ precursors in alkaline solutions. The catalysts were characterized by TEM, XRD, XPS, nitrogen sorption, ICP-OES, H2-TPD and CO adsorption. The as-prepared 5 wt% Ru2.5Ni2.5/Al2O3 exhibits the best catalytic activity compared to the as-prepared catalysts with the highest metal dispersion and minimum average particle size of 5.210 nm. The hydrogenation activation energy for 5 wt% Ru2.5Ni2.5/Al2O3 at 150–180 °C was estimated to be approximately 12.95 kJ mol−1. No obvious degradation was observed after 5 cycles of hydrogenation for the 5 wt% Ru2.5Ni2.5/Al2O3 catalyst, indicating that the catalyst has applicable stability. The hydrogen spillover has been proved to occur more easily on the Ru–Ni clusters by theoretical calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...