Cooperative acid–base bifunctional ordered porous solids in sequential multi-step reactions: MOF vs. mesoporous silica†
Abstract
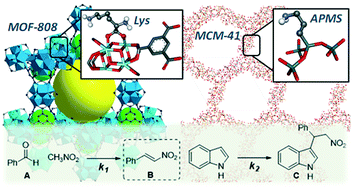
Two different catalytic platforms, MOF and mesoporous silica, are compared as porous support for basic amino groups. Lysine grafted to MOF-808 is reported for the first time as a highly basic catalyst, showing a competitive performance with respect to benchmark aminoalkoxysilane grafted to MCM-41. Kinetic analysis demonstrates the beneficial effect of acid sites, Zr or Al, on both types of porous solids, resulting in acid–base cooperative effects that stabilize the transition states of two sequential C–C bond forming steps for the one-pot synthesis of substituted indole.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...