Real-time monitoring of surface acetone enolization and aldolization†
Abstract
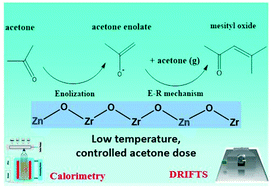
We report the identification of acetone enolate and its subsequent aldolization. The real-time evolution of surface species monitored by in situ DRIFTS of surface acetone (-d6) reactions shows clear spectroscopic evidence of the formation of acetone enolate and its subsequent aldolization via a dominant Eley–Rideal type mechanism on Zn1Zr10Oz.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...