Redox mediators as charge agents for changing electrochemical reactions†
Abstract
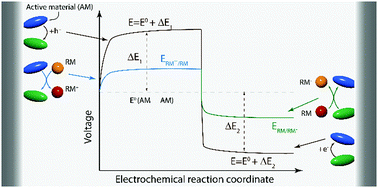
Redox mediators (RMs) play pivotal roles in enhancing the performance of electrochemical energy storage and conversion systems. Unlike the widely explored areas of electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, and electrolyte additives, RMs have received little attention. This review provides a comprehensive discussion toward understanding the effects of RMs on electrochemical systems, underlying redox mechanisms, and reaction kinetics both experimentally and theoretically. Our discussion focuses on the roles of RMs in various electrochemical systems such as lithium-ion batteries, Li–O2 batteries, Li–S batteries, decoupling electrolysis, supercapacitors, and microbial fuel cells. Depending on the reaction regions where the RMs become active, we can classify them into bulk, solid–solid interfacial, solid–liquid interfacial, and cell-unit RMs. The prospect of developing RMs with effective charge transfer properties along with minimal side-effects is an exciting research direction. Moreover, the introduction of an efficient RM into an electrochemical system can fundamentally change its chemistry; in particular, the electrode reaction polarization can be considerably decreased. In this context, we discuss the key properties of RMs applied for various purposes, and the main issues are addressed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...