Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: an updated review (2010–2020)
Abstract
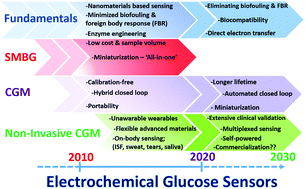
While over half a century has passed since the introduction of enzyme glucose biosensors by Clark and Lyons, this important field has continued to be the focus of immense research activity. Extensive efforts during the past decade have led to major scientific and technological innovations towards tight monitoring of diabetes. Such continued progress toward advanced continuous glucose monitoring platforms, either minimal- or non-invasive, holds considerable promise for addressing the limitations of finger-prick blood testing toward tracking glucose trends over time, optimal therapeutic interventions, and improving the life of diabetes patients. However, despite these major developments, the field of glucose biosensors is still facing major challenges. The scope of this review is to present the key scientific and technological advances in electrochemical glucose biosensing over the past decade (2010–present), along with current obstacles and prospects towards the ultimate goal of highly stable and reliable real-time minimally-invasive or non-invasive glucose monitoring. After an introduction to electrochemical glucose biosensors, we highlight recent progress based on using advanced nanomaterials at the electrode–enzyme interface of three generations of glucose sensors. Subsequently, we cover recent activity and challenges towards next-generation wearable non-invasive glucose monitoring devices based on innovative sensing principles, alternative body fluids, advanced flexible materials, and novel platforms. This is followed by highlighting the latest progress in the field of minimally-invasive continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) which offers real-time information about interstitial glucose levels, by focusing on the challenges toward developing biocompatible membrane coatings to protect electrochemical glucose sensors against surface biofouling. Subsequent sections cover new analytical concepts of self-powered glucose sensors, paper-based glucose sensing and multiplexed detection of diabetes-related biomarkers. Finally, we will cover the latest advances in commercially available devices along with the upcoming future technologies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...