Thermodynamics of cell penetrating peptides on lipid membranes: sequence and membrane acidity regulate surface binding†
Abstract
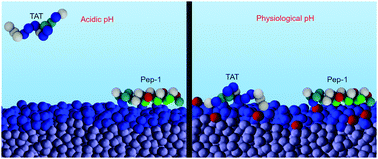
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are molecules that traverse cell membranes and facilitate the cellular uptake of nano-sized cargoes. In this work we characterize the adsorption of amphipathic and purely cationic CPPs on membranes containing acidic lipids. We describe how the peptide primary sequence, the location of amino-acids within the sequence, the membrane composition, and the pH of the environment, determine both the surface concentration of the peptides and the molecular organization of the interface. Our results are obtained by applying a molecular theory that takes into account the size, shape, protonation state, charge distribution and conformational flexibility of the peptides, as well as the acid–base chemistry of the lipids. We find that peptide adsorption and binding free energy result from a balance between electrostatic and van der Waals interactions, and between chemical and entropic effective forces. We observe that, within a range of physiologically relevant parameters, acidic lipids respond to pH in ways that fully promote or deplete the surface accumulation of CPPs. Membrane acidity emerges thus as a crucial parameter to consider when designing CPP-based cargo-delivery vehicles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...