The role of hydrogen bond donor and water content on the electrochemical reduction of Ni2+ from solvents – an experimental and modelling study†
Abstract
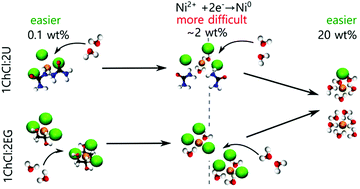
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) are hygroscopic liquids composed of a hydrogen bond donor (HBD) and acceptor (HBA). Their physical, chemical and electrochemical properties can be tailored to use them as solvents for different applications, i.e. electrodeposition, catalysis, extraction, etc. This can be done by changing the HBD, as well by adding water. However, the interrelated influence of H2O and HBD on the structure of the electrolyte, and on the behavior of the active species is not fully understood. In this work, we select nickel electrodeposition as a case study and we combine electrochemical techniques (cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry) with UV-vis spectroscopy and molecular dynamics to understand the influence of water and HBD on the electrochemical behaviour of DESs. The unique combination of these different experimental and modelling techniques provides new insights into the field. The addition of H2O changes, not only the interactions between the constituents of the liquid, but also the coordination of metal cations, which is reflected in the electrochemical performance of different DESs. More importantly, we show that, in the presence of very little (between 0.1 wt% and 2.8 wt%) and high (>4.5 wt%) water contents, DESs behave differently, and the changes in their electrochemical behavior are caused by both the complexation of metal cations and the electrolyte transport properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...