Intermolecular interactions of cn-716 and acyl-KR-aldehyde dipeptide inhibitors against Zika virus
Abstract
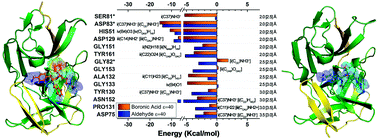
The emergent Zika virus (ZIKV) infection has become a threat to global health due to its association with severe neurological abnormalities, namely Guillain–Barré Syndrome (GBS) in adults and Congenital Zika virus Syndrome (CZS) in neonates. Many studies are nowadays being conducted to find an effective antiviral drug against ZIKV. In particular, NS2B–NS3 protease is an attractive drug target due to its essential function in viral replication, although a drug is not yet commercially available. In this context, we present here a comparative structural study, based on quantum chemistry calculations, to analyze the intermolecular binding energies between the crystallographic structure of NS2B–NS3 protease and dipeptide boronic acid (cn-716) and aldehyde (acyl-KR-aldehyde) peptidomimetic inhibitors, by using the molecular fractionation with conjugate caps (MFCC) scheme within the density functional theory (DFT) formalism. Most intermolecular interactions in cn-716/NS2B–NS3 (acyl-KR-aldehyde/NS2B–NS3) are due to the amino acid residues Asp83*, His51, Asp129, Ser81*, Gly133, Ala132, Tyr161, Asn152 and Asp75 (Asp83*, Asp129, His51, Asn152, Tyr161, Tyr130, Gly153, Gly151, Asp75, Pro131, and Gly82). Additionally, we have considered missense mutation analysis of these residues to evaluate the destabilization and the increase of the flexibility of the protease, showing that mutation of the residues Tyr161 and Tyr130 causes more impact. Our simulations are a valuable tool for a better understanding of the binding mechanism of recognized inhibitors of NS2B–NS3 protease, and can lead to the rational design and development of novel anti-Zika drugs with improved efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...