The melting temperature of nanorods: diameter and length dependences
Abstract
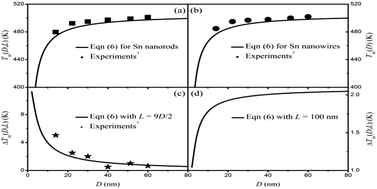
A thermodynamic model for the diameter- and length-dependent melting temperature Tm(D,L) of nanorods has been proposed from the perspective of the Gibbs free energy together with the size-dependent interface energy, where D and L denote the diameter and the length of the nanorods. As the model describes, Tm(D,L) decreases with a decrease in D and L, where the diameter effect is dominant while the length effect is secondary. Agreements between model predictions and the available experimental and molecular dynamics simulation results can be found for Sn and Cu nanorods, which enabled us to determine the size dependence of the magnetostructural transition temperature in MnBi nanorods. This work is helpful for the design and application of nanoscale devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...