CO2 capture, activation and dissociation on the Ti2C surface and Ti2C MXene: the role of surface structure†
Abstract
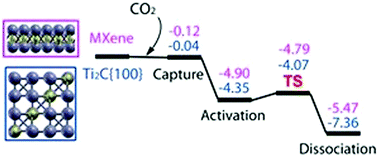
Atmospheric CO2 is one of the main components of the greenhouse effect. To overcome this problem there are ongoing efforts to convert CO2 to some other useful and harmless products. The capture, activation and dissociation of CO2 are the preliminary steps in this process. In an effort to understand the role of surface composition and structure in CO2 adsorption and dissociation, in this work, with the help of first principles density functional theory based calculations, we have studied the same on the {100} surface of cubic Ti2C and MXene (also the {0001} surface of trigonal Ti2C). Our results show that CO2 undergoes barrierless chemisorption on both of these surfaces with a preference towards {100} cubic Ti2C. We attribute the reason for this to a lower value of the work function of the {100} surface. Furthermore, on MXene, the barrier for CO2 dissociation is lower compared to that on the {100} surface. Coverage dependent CO2 chemisorption studies on these two surfaces show that on the Ti2C surface the CO2 molecules form clusters around the C-vacancies while on MXene they are uniformly spread on the surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...