Stacking interactions of resonance-assisted hydrogen-bridged rings and C6-aromatic rings†
Abstract
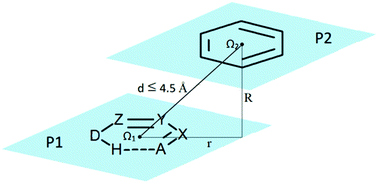
Stacking interactions between six-membered resonance-assisted hydrogen-bridged (RAHB) rings and C6-aromatic rings were systematically studied by analyzing crystal structures in the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD). The interaction energies were calculated by quantum-chemical methods. Although the interactions are stronger than benzene/benzene stacking interactions (−2.7 kcal mol−1), the strongest calculated RAHB/benzene stacking interaction (−3.7 kcal mol−1) is significantly weaker than the strongest calculated RAHB/RAHB stacking interaction (−4.7 kcal mol−1), but for a particular composition of RAHB rings, RAHB/benzene stacking interactions can be weaker or stronger than the corresponding RAHB/RAHB stacking interactions. They are also weaker than the strongest calculated stacking interaction between five-membered saturated hydrogen-bridged rings and benzene (−4.4 kcal mol−1) and between two five-membered saturated hydrogen-bridged rings (−4.9 kcal mol−1). SAPT energy decomposition analyses show that the strongest attractive term in RAHB/benzene stacking interactions is dispersion, however, it is mostly canceled by a repulsive exchange term; hence the geometries of the most stable structures are determined by an electrostatic term.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...