Exploration of the potential energy surfaces of small ethanol clusters†
Abstract
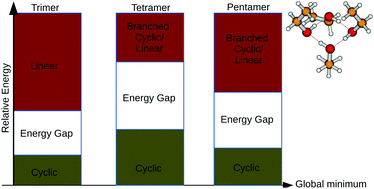
The potential energy surfaces (PESs) of the ethanol clusters become increasingly complex as the cluster size increases. This is mainly due to the fact that there are up to three stable structures on the PES of the ethanol monomer yielding a huge number of possible structures of the ethanol clusters. In this work, we have thoroughly explored the PESs of neutral ethanol clusters from dimer to pentamer. For each cluster size, we have identified all possible combinations of the three monomers to build a structure of that cluster size. For each combination, we have used ABCluster to generate initial guessed geometries. These geometries have been fully optimized at the MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ level of theory. The results show that the PESs of the neutral ethanol clusters are symmetric due to enantiomerism of the clusters. For each cluster size, several isomers have been located as global minima energy structures. Globally, we have found that cyclic structures are the most stable, followed by branched cyclic and linear structures. The branched linear structures are found to be among the least stable structures on the PESs of the neutral ethanol clusters. The infrared spectra of the most stable structures are calculated and compared to experiment. The calculated infrared spectra are found to be in qualitative agreement with experiment. In addition, we have calculated the binding energies of the investigated ethanol clusters using MP2, some density functional theory (DFT) functionals (MN15, ωB97XD and PW6B95D3) and DLPNO-CCSD(T)/CBS levels of theory. As a result, we have found that the PW6B95D3 functional has the smallest mean absolute deviation (MAD) as compared to ωB97XD and MN15, when benchmarked to the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/CBS. Thus, we recommend the PW6B95D3 functional for affordable, yet accurate, exploration of neutral ethanol clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...