Kinetic instability of sulfurous acid in the presence of ammonia and formic acid†
Abstract
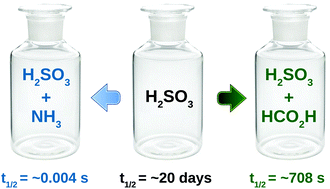
In the present work, we have studied the effect of ammonia and formic acid on the kinetic stability of sulfurous acid using high level ab initio calculations. Our investigation reveals that the decomposition reaction of sulfurous acid becomes barrierless in the presence of both ammonia and formic acid. The half-life of the isolated sulfurous acid is estimated to be ∼20 days at room temperature, which becomes only ∼4.0 × 10−3 s and ∼7.08 × 102 s in the presence of ammonia and formic acid, respectively. These results indicate that, in the presence of ammonia, the stability of sulfurous acid reduces substantially at room temperature. The temperature dependency of the rate constant values indicates that, in the presence of ammonia and formic acid, the reaction has a negative activation energy, while the uncatalyzed and water catalyzed channels have a positive activation energy. We have also studied the pressure dependency of the catalyzed reaction, which suggests that the ammonia catalyzed channel is most sensitive towards the pressure change, as the values of the bimolecular rate constant (kbi) for this channel were found to be increased by an order of magnitude on going from 0.1 to 10 atm of pressure. Whereas, for the FA and WM catalyzed channels the changes in kbi with pressure were negligible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...