Understanding the electronic properties of BaTiO3 and Er3+ doped BaTiO3 films through confocal scanning microscopy and XPS: the role of oxygen vacancies†
Abstract
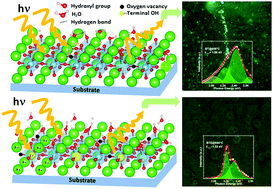
Photonic and electronic properties exist inherently in ferroelectric barium titanate (BaTiO3); severe luminescence quenching also exists due to the insufficient confinement of excitons. In this sense, high optical emission can only be achieved by its chemical and structural modification. Thin BaTiO3 and Er:BaTiO3 films were grown by the spin coating method on a glass substrate at room temperature. Self-trapping of excitons in the thin BaTiO3 film and its structural modification due to the doping with Er3+ ions (Er:BaTiO3) are verified using scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy (SCFM), where self-trapping excitons never occured in its pure state. By thermal treatment and doping (BaTiO3 and Er:BaTiO3) we obtained localization of the excitons, which would further induce lattice strain around the surface defects, to accommodate the self-trapped excitons. With such a self-trapped state, the structure of BaTiO3 generates broadband emission of several overlapping bands between 1.95 and 2.65 eV at room temperature, while the structure Er:BaTiO3 showed defined emission bands at 2.24 and 2.35 eV, with very weak contributions of the emission due to the self-trapping state. The influence of the variation of the excitation wavelength using 1PE and 2PE on the emission bands of BaTiO3 and Er:BaTiO3 is also investigated. The results of enhanced emission bands suggest a clear dependence of the emission intensity on the excitation energy, where a ∼3 fold enhancement in emission has been demonstrated under Er3+ (1.55 eV) excitation, which can be attributed to effective energy transfer between the Er3+ ions. As a result, it is concluded that the developed BaTiO3 and Er:BaTiO3 can pave the way for future photonic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...