Embedding of atoms into the nanopore sites of the C6N6 and C6N8 porous carbon nitride monolayers with tunable electronic properties†
Abstract
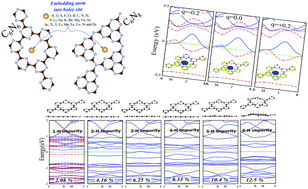
Using first-principles calculations, we study the effect of embedding various atoms into the nanopore sites of both C6N6 and C6N8 monolayers. Our results indicate that the embedded atoms significantly affect the electronic and magnetic properties of C6N6 and C6N8 monolayers and lead to extraordinary and multifarious electronic properties, such as metallic, half-metallic, spin-glass semiconductor and dilute-magnetic semiconductor behaviour. Our results reveal that the H atom concentration dramatically affects the C6N6 monolayer. On increasing the H coverage, the impurity states also increase due to H atoms around the Fermi-level. C6N6 shows metallic character when the H atom concentration reaches 6.25%. Moreover, the effect of charge on the electronic properties of both Cr@C6N6 and C@C6N8 is also studied. Cr@C6N6 is a ferromagnetic metal with a magnetic moment of 2.40 μB, and when 0.2 electrons are added and removed, it remains a ferromagnetic metal with a magnetic moment of 2.57 and 2.77 μB, respectively. Interestingly, one can observe a semi-metal, in which the VBM and CBM in both spin channels touch each other near the Fermi-level. C@C6N8 is a semiconductor with a nontrivial band gap. When 0.2 electrons are removed, it remains metallic, and under excess electronic charge, it exhibits half-metallic behaviour.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...