Ion and radical chemistry in (H2O2)N clusters†
Abstract
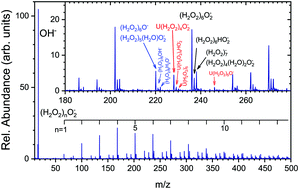
We investigate the ionization induced chemistry of hydrogen peroxide in (H2O2)N clusters generated after the pickup of individual H2O2 molecules on large free ArM, ![[M with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_004d_0304.gif) ≈ 160, nanoparticles in molecular beams. Positive and negative ion mass spectra are recorded after an electron ionization of the clusters at energies 5–70 eV and after a slow electron attachment (below 4 eV), respectively. The spectra demonstrate that (H2O2)N clusters with N ≥ 20 are formed on argon nanoparticles. This is the first experimental report on hydrogen peroxide clusters in molecular beams. The major negative cluster ion series (H2O2)nO2− indicates O2− ion formation. The dissociative electron attachment to H2O2 molecules in the gas phase yielded only OH− and O− (Nandi et al., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 373, 454). These ions and the series containing them are much less abundant in the clusters. We propose a sequence of ion–molecule and radical reactions to explain the formation of O2−, HO2− and other ions observed in the negatively charged cluster ion series. Since hydrogen peroxide plays an important role in many areas of chemistry from the Earth's atmosphere to biological tissues, our study opens new horizons for experimental investigations of hydrogen peroxide chemistry in complex environments.
≈ 160, nanoparticles in molecular beams. Positive and negative ion mass spectra are recorded after an electron ionization of the clusters at energies 5–70 eV and after a slow electron attachment (below 4 eV), respectively. The spectra demonstrate that (H2O2)N clusters with N ≥ 20 are formed on argon nanoparticles. This is the first experimental report on hydrogen peroxide clusters in molecular beams. The major negative cluster ion series (H2O2)nO2− indicates O2− ion formation. The dissociative electron attachment to H2O2 molecules in the gas phase yielded only OH− and O− (Nandi et al., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 373, 454). These ions and the series containing them are much less abundant in the clusters. We propose a sequence of ion–molecule and radical reactions to explain the formation of O2−, HO2− and other ions observed in the negatively charged cluster ion series. Since hydrogen peroxide plays an important role in many areas of chemistry from the Earth's atmosphere to biological tissues, our study opens new horizons for experimental investigations of hydrogen peroxide chemistry in complex environments.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...