Specific ion effects on the enzymatic activity of alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
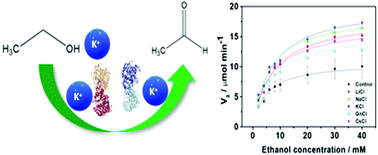
The enzymatic activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) in the presence of a range of electrolytes is investigated. In the presence of 150 and 200 mM cations a substantial increase in activity following the series GnCl < CsCl < KCl ∼ NaCl < LiCl was observed with a 69% increase in the presence of KCl 200 mM with respect to the salt-free solution. In the presence of 150 and 200 mM anions the increase in activity followed an ion specific trend NaF ∼ NaCl ∼ NaBr > no salt > NaClO4 > NaSCN with a peak in activity increase of 75% in the presence of NaBr. The values of the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) did not show any significant ion specific effect, while the maximum rate (Vmax) of ethanol oxidation to acetaldehyde was strongly ion specific. The changes in specific activity and Vmax in the presence of anions likely arises from ion specific interactions with charged residues in the active site of ADH. The data indicate that the enzymatic activity of alcohol dehydrogenase can be modulated by the nature of electrolytes at physiological concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...