A theoretical study on the binding and electrolytic splitting of hydrogen fluoride on Ni(111) and Ni(211)†
Abstract
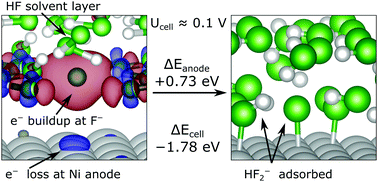
The Simons process is widely used in the production of fluorinated organic molecules. It is believed to proceed through the electrochemical fluorination of a Ni anode using hydrogen fluoride (HF), forming an amorphous nickel fluoride film of unknown chemical structure NixFy. By using periodic density functional theory calculations, we describe the initial binding of HF to the Ni(111) and (211) surfaces in terms of binding energies and mechanisms. We start with the binding of a single HF molecule to the surfaces, with or without point defects and find that the binding is most efficient at protruding Ni atoms which provide a coordination site for the F atom. Subsequently, we study the structure of a fully covered HF/Ni interface and find that HF–HF hydrogen bonding dominates over HF adsorption to Ni. Finally, we model the electrolyte–electrode interface as an HF layer on Ni(111) with the anodic and cathodic adsorption of F− and H+ onto charged electrodes. The splitting of HF is found to be exothermic, even at low cell potentials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...