Interfacial tension and mechanism of liquid–liquid phase separation in aqueous media†
Abstract
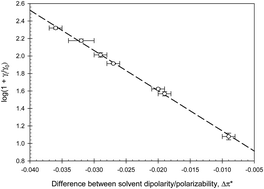
The organization of multiple subcellular compartments is controlled by liquid–liquid phase separation. Phase separation of this type occurs with the emergence of interfacial tension. Aqueous two-phase systems formed by two non-ionic polymers can be used to separate and analyze biological macromolecules, cells and viruses. Phase separation in these systems may serve as the simple model of phase separation in cells also occurring in aqueous media. To better understand liquid–liquid phase separation mechanisms, interfacial tension was measured in aqueous two-phase systems formed by dextran and polyethylene glycol and by polyethylene glycol and sodium sulfate in the presence of different additives. Interfacial tension values depend on differences between the solvent properties of the coexisting phases, estimated experimentally by parameters representing dipole–dipole, ion–dipole, ion–ion, and hydrogen bonding interactions. Based on both current and literature data, we propose a mechanism for phase separation in aqueous two-phase systems. This mechanism is based on the fundamental role of intermolecular forces. Although it remains to be confirmed, it is possible that these may underlie all liquid–liquid phase separation processes in biology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
