The key structural features governing the free radicals and catalytic activity of graphite/graphene oxide†
Abstract
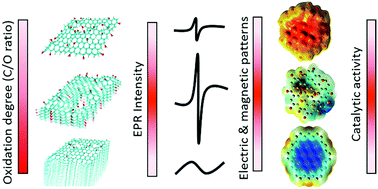
The presence of unpaired electrons (radicals) due to structural defects is believed to contribute to the catalytic reactivity of carbon materials. Graphite oxide and graphene oxide (GO) consist of significant structural defects and hence are considered more reactive than graphite and graphene. However, the relationship between their radical content/reactivity and their physical and chemical structures remains unknown, which limits the fabrication of high efficiency carbon-based catalysts. In this work, we progressively oxidize graphite to achieve graphite oxide and GO with different levels of oxidation and different sizes. It is observed that a maximal radical content can be achieved on graphite oxide with a C/O ratio of ca. 3.0 and a thickness of around 50 nm. Such a graphite oxide contains about 45% of π bonds and 38% of oxygenated bonds, respectively. Thinner or thicker sheets have lower radical contents due to over or insufficient oxidation, respectively. Single GO sheets with high radical contents can only be produced through a combination of oxidation and reduction. The catalytic activity of the graphite/graphene oxide for phenol degradation was found to be linearly correlated to their radical contents. The observations are significant for the advancement of carbon-based metal-free catalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...