Enhanced thermopower in covalent graphite–molecule contacts†
Abstract
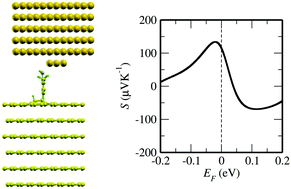
The Seebeck effect is very attractive for technological applications as it leads to the direct conversion of heat into electricity. One of the key quantities determining the efficiency of such conversion is the thermopower S. In this paper we explore theoretically what electronic properties are responsible for the Seebeck effect in molecular junctions with graphite or graphene electrodes. We propose that S can be enhanced because of the combined effect of the dip in the density of states at the Fermi energy of these materials and the molecular resonance. Then to understand the impact of the covalent vs. non-covalent molecule–carbon bonding we calculate from first principles the electronic and transport properties of graphite/molecule/Au junctions, where both types of bonding have been reported experimentally. We ultimately predict that S is about 120 μV K−1 at room temperature for a 3,5-dimethyl-4-aminobenzene (DMAB) molecule covalently attached to the graphite electrode. This value is one order of magnitude larger than the typical values measured to date for molecular junctions and it is a signature of the direct C–C molecule–graphite bond. Finally we also demonstrate how one can control not just the absolute magnitude of S, but also its sign by designing the graphite–molecule contact. Our results lead the way towards the use of junctions with molecules covalently attached to a C-based substrate as possible new improved platforms for molecular thermoelectric devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...