Absorption spectra of xanthines in aqueous solution: a computational study†
Abstract
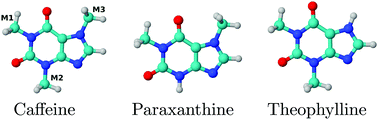
We present a detailed computational analysis of the UV/Vis spectra of caffeine, paraxanthine and theophylline in aqueous solution. A hierarchy of solvation approaches for modeling the aqueous environment have been tested, ranging from the continuum model to the non-polarizable and polarizable quantum mechanical (QM)/molecular mechanics (MM) models, with and without the explicit inclusion of water molecules in the QM portion. The computed results are directly compared with the experimental data, thus highlighting the role of electrostatic, polarization and hydrogen boding solute–solvent interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...