The role of cations in uranyl nanocluster association: a molecular dynamics study†
Abstract
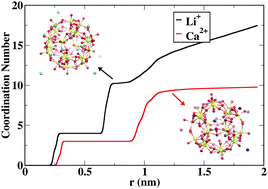
Actinyl ions can self-assemble in aqueous solution to form closed cage clusters ranging from 1.5 to 4.0 nm in diameter. The self-assembly, stability, and behavior of the nanoclusters depend on the nature of the aqueous environment, such as the pH and cations present. In this work, a classical force field for [(UO2)20(O2)30]20− (U20) peroxide nanoclusters in aqueous solution was developed from quantum-mechanical calculations. Using molecular dynamics simulations, the preferred binding sites of six cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+, and Ca2+) to the nanocluster were determined. Replica exchange molecular dynamics was used to equilibrate the structure and determine the equilibrium distribution of cations and water with respect to the nanocluster cage. In addition, the free energy barriers associated with cations entering the cluster were computed. Finally, the association of two cages was investigated by computing the free energy as a function of intercage distance. The free energy profiles reveal that the nanoclusters prefer to be associated when neutralized with divalent cations, but do not associate when neutralized with monovalent cations. This could explain the formation of tertiary structures observed experimentally.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...