Solvate ionic liquids based on lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide–glyme systems: coordination in MD simulations with scaled charges†
Abstract
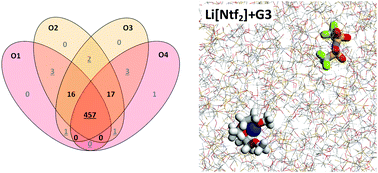
Equimolar mixtures of lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Li[NTf2]) with triglyme or tetraglyme (small oligoethers) are regarded as a new class of ionic liquids, the so-called solvate ionic liquids. In these mixtures, the glyme molecules wrap around the lithium ions forming crown-ether like [Li(glyme)1]+ complex cations. New molecular dynamics (MD) simulations suggest that the lithium–glyme coordination is stronger than that predicted in a former MD study [K. Shimizu, et al., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 22321–22335], whereas lithium–NTf2 connections are weaker. The differences between the present and the previous study arise from different starting conditions. Both studies employed charges scaled by a factor of 0.8. As shown by the comparison of MD simulations with and without reduced charges to experiments, charge scaling is necessary in order to obtain data close to experimental results.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...