Synergistic effect of various intermolecular interactions on self-assembly and optoelectronic behaviour in co-crystals/salts of tetrabromoterephthalic acid: a report on their structure, theoretical study and Hirshfeld surface analysis†
Abstract
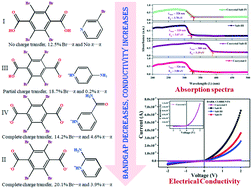
The rational design of organic opto-electronic materials has been one of the prime focuses in recent times, and halogen interactions have become a major tool in crystal engineering to design multi-component organic co-crystals/salts. Tetrabromoterephthalic acid (TBTA), which is able to participate in both hydrogen bonding and halogen bonding, has been used as a co-crystallizing agent to synthesize four different organic co-crystals/salts, TBTA-3-bromopyridine (co-crystal I), TBTA·TBTA2−-2(2-aminopyridine+)·2H2O (co-crystal salt II), TBTA−-4-aminopyridine+·H2O (salt III) and TBTA·TBTA2−-2(nicotinamide+)·2H2O (co-crystal salt IV), by a conventional solvent evaporation method. These compounds were characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SC-XRD), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and spectral and thermal studies. Molecular and supramolecular structural analyses reveal that TBTA interacts with the pyridyl-containing co-formers through hydrogen bonding and exploits several types of halogen bonding (Br⋯O, Br⋯H, Br⋯Br, Br⋯π interactions etc.) and π⋯π interactions to assemble in the solid state. TBTA utilizes Br⋯π interactions to assemble with other co-formers while it utilizes Br⋯O interactions and preferably type I Br⋯Br interactions to assemble with each other in these co-crystals/salts. The supramolecular behaviour of TBTA within these co-crystals/salts analyzed by Hirshfeld surface analysis and associated 2D fingerprint plots also corroborates the crystallographic supramolecular structural patterns. Theoretical analysis has been carried out for geometry optimization and bandgap calculations which were then compared with the optical bandgap values. Charge-separated hydrogen bonding and π⋯ interactions (Br⋯π and π⋯π interactions) have a significant impact on the optical and electrical properties of these samples. Solid-state luminescence studies reveal that all compounds show a blue shift. Electrical conductivity measurements on the ITO/sample/Al sandwich structures of these supramolecular complexes reveal Schottky barrier diode behaviour and photoresponsivity under illumination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...