Full-visible-spectrum lighting realized by a novel Eu2+-doped cyan-emitting borosilicate phosphor
Abstract
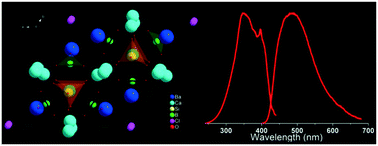
White light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) have become one of the first choices in the field of lighting due to their unique advantages. In the traditional system of near-ultraviolet (NUV) chips combined with blue/green/red-emitting phosphors, the partial absence of a blue-green cavity makes it difficult to achieve full-spectrum emission. Accordingly, cyan-emitting phosphors can effectively compensate for this missing part. Therefore, it is necessary and urgent to explore the cyan-emitting phosphor with excellent luminous performance. Herein, we have designed and prepared a novel cyan-emitting borosilicate phosphor Ba3Ca4(BO3)3(SiO4)Cl:xEu2+ (BCBS:xEu2+). Its crystal structure was determined by powder X-ray diffraction and Rietveld methods. The BCBS:xEu2+ phosphors have a wide excitation band covering the UV-NUV region and can emit a broad cyan light. The emission peaks at 488 nm have a large full width at half maximum (FWHM) of 118 nm, excited by 350 nm. There are three different Eu2+ luminescence centers in BCBS:xEu2+, which are determined by analyzing the structure and decay curves. The optimal concentration was x = 0.04 and the quantum efficiency of the BCBS:0.04Eu2+ sample was 31.2%. In addition, by combining BCBS:Eu2+, Sr2SiO4:Eu2+ and (Ca,Sr)AlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphors with a 395 nm NUV chip, a WLED lamp was obtained. The emitted white light can display excellent performances of CIE = (0.3655, 0.3641), CCT = 4337 K and CRI = 90.1. All the results demonstrate that the BCBS:Eu2+ phosphors have potential applications in full-visible-spectrum lighting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...