Halogenide anions as halogen and hydrogen bond acceptors in iodopyridinium halogenides†
Abstract
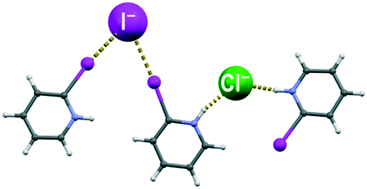
In order to study halogenide anions simultaneously acting as hydrogen bond and halogen bond acceptors, we have prepared and crystallised halogenide salts (chlorides, bromides and iodides) of the three isomers of iodopyridine, 2-iodopyridine (2-IPy), 3-iodopyridine (3-IPy) and 4-iodopyridine (4-IPy). In all nine structures the pyridinium cations and the halogenide anions are interconnected through C–I⋯X− halogen and N–H⋯X− hydrogen bonds (X = Cl, Br, I). Based on the trend observed in the relative shortening of the two interactions, both halogen and hydrogen bonds seem to be decreasing in strength with the size of the halogenide anion, although the decrease is apparently more pronounced for hydrogen bonds. To study this further, we have performed a CSD study of structures comprising a halogenide and both hydrogen and halogen bond donors, which has indicated a tendency of chloride towards hydrogen and of iodide towards halogen bonds, in accord with our experimental results. Additionally, we have obtained crystals of ((2-IPyH)2 Cl I), the first example of a double salt comprising both hydrogen and halogen bond donors and two different halogenides. In this structure, the halogen bonds were formed exclusively with the iodide anion, while the hydrogen bonds were formed only with the chloride anion.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...