Hollow porous Cu–Au particles with high catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol†
Abstract
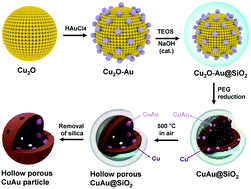
A Cu-based bimetallic hollow structure can be effectively used to enhance the selective oxidation and electrocatalytic activity of a catalyst and to reduce its cost. In this paper, we developed a facile and scalable method for the construction of CuAu bimetallic hollow particles from Cu2O nanoparticle aggregates (NPAs). The synthetic process includes Au growth on the Cu2O NPA surface and silica encapsulation, which is followed by polyol reduction of Cu2O, calcination in air and etching of the SiO2 layer. The obtained hollow CuAu NPs (average diameter of 540 nm and wall thickness of 60 nm) outperform hollow Cu NPs in terms of catalytic activity in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol by NaBH4 in aqueous solution. The activity factors (K = 354 and 255 s−1 g−1) are 2.4 and 1.7 times larger than that of the hollow Cu catalyst, depending on the Au content in the CuAu particles. In addition, the prepared catalyst was stable in the reaction system and can be recycled via centrifugation without a significant loss of catalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...