R-Substituent induced structural diversity, synergistic effect and highly selective luminescence sensing for Fe3+ detection by post-synthetically modified Cd-MOFs†
Abstract
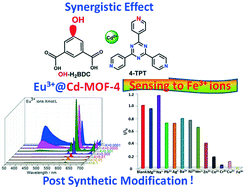
The self-assembly of 5-substituted isophthalic acid (R-H2BDC, R = H, NO2, Me, OH and tBu), CdII ions and 2,4,6-tris(3-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine (3-TPT) or 2,4,6-tris(4-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine (4-TPT) under solvothermal conditions yields six Cd-MOFs: {[Cd(BDC)(4-TPT)]·1.5H2O}n (Cd-MOF-1), {[Cd(NO2-BDC)(4-TPT)]·2H2O}n (Cd-MOF-2), {[Cd(Me-BDC)(4-TPT)]·2H2O}n (Cd-MOF-3),{[Cd(OH-BDC)(4-TPT)]·2.5H2O}n (Cd-MOF-4), {[Cd(tBu-BDC)(4-TPT)2/3]·DMF}n (Cd-MOF-5), and {[Cd(BDC)(3-TPT)2/3]·3H2O}n (Cd-MOF-6), (where H2BDC = isophthalic acid, NO2-BDC = 5-nitroisophthalic acid, Me-BDC = 5-methylisophthalic acid, OH-BDC = 5-hydroxyisophthalic acid, tBu-BDC = 5-tert-butylisophthalic acid, 3-TPT = 2,4,6-tris(3-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine and 4-TPT = 2,4,6-tris(4-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine). All the compounds are constructed from dimeric Cd2(OCO)2 units, connected by mixed R-H2BDC and n-TPT ligands into three-dimensional frameworks. Cd-MOF-1, 2 and 3 are isostructural, in which the Cd2(OCO)2 units are bridged into 1D chains extending along the [1 1 0] and [−1 1 0] directions, respectively, and are then further interlinked by 4-TPT ligands into three-dimensional networks with a CdS net topology. Cd-MOF-4 exhibits a three-dimensional framework with a pcu topology, in which the dimeric Cd2(OCO)2 units are firstly connected into two-dimensional Cd(OH-BDC)n sheets, and further “pillared” by 4-TPT into a three-dimensional network. In Cd-MOF-5 and 6, the Cd2(OCO)2 units are firstly linked into a three-dimensional NbO net by tBu-BDC/BDC ligands, which are further accommodated by the size-matching trigonal 3-TPT/4-TPT ligands into a novel (3,8)-connected three-dimensional net. Interestingly, via the synergistic effect of open hydroxyl and pyridyl groups, Cd-MOF-4 can be functionalized by Eu3+ ions by post-synthetic modification, and the resulting 0.001Eu3+@Cd-MOF-4 phosphor serves as a highly selective and sensitive probe for detection and recognition of Fe3+ ions through the luminescence quenching effect in aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...